A better confusion matrix with python
The Confusion Matrix is a nice way to summarize the results from a binary classification problem. While scikit-learn offers a nice method to compute this matrix (for multiclass classification, as well), I’m not aware of a built-in method that shows the relevant statistics from the confusion matrix. Often the matrix is just shown, color-coded according to entry values.
I wrote a little script for displaying the confusion matrix (as computed by scikit-learn), using matplotlib. The results look like this:
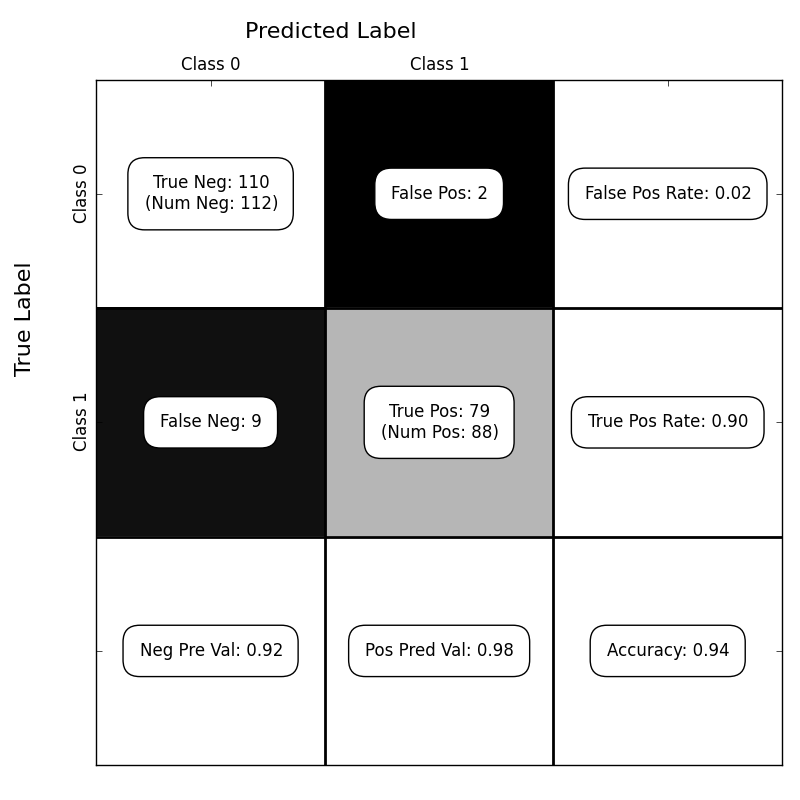
Here’s the function for generating the confusion matrix:
def show_confusion_matrix(C,class_labels=['0','1']):
"""
C: ndarray, shape (2,2) as given by scikit-learn confusion_matrix function
class_labels: list of strings, default simply labels 0 and 1.
Draws confusion matrix with associated metrics.
"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
assert C.shape == (2,2), "Confusion matrix should be from binary classification only."
# true negative, false positive, etc...
tn = C[0,0]; fp = C[0,1]; fn = C[1,0]; tp = C[1,1];
NP = fn+tp # Num positive examples
NN = tn+fp # Num negative examples
N = NP+NN
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.imshow(C, interpolation='nearest', cmap=plt.cm.gray)
# Draw the grid boxes
ax.set_xlim(-0.5,2.5)
ax.set_ylim(2.5,-0.5)
ax.plot([-0.5,2.5],[0.5,0.5], '-k', lw=2)
ax.plot([-0.5,2.5],[1.5,1.5], '-k', lw=2)
ax.plot([0.5,0.5],[-0.5,2.5], '-k', lw=2)
ax.plot([1.5,1.5],[-0.5,2.5], '-k', lw=2)
# Set xlabels
ax.set_xlabel('Predicted Label', fontsize=16)
ax.set_xticks([0,1,2])
ax.set_xticklabels(class_labels + [''])
ax.xaxis.set_label_position('top')
ax.xaxis.tick_top()
# These coordinate might require some tinkering. Ditto for y, below.
ax.xaxis.set_label_coords(0.34,1.06)
# Set ylabels
ax.set_ylabel('True Label', fontsize=16, rotation=90)
ax.set_yticklabels(class_labels + [''],rotation=90)
ax.set_yticks([0,1,2])
ax.yaxis.set_label_coords(-0.09,0.65)
# Fill in initial metrics: tp, tn, etc...
ax.text(0,0,
'True Neg: %d\n(Num Neg: %d)'%(tn,NN),
va='center',
ha='center',
bbox=dict(fc='w',boxstyle='round,pad=1'))
ax.text(0,1,
'False Neg: %d'%fn,
va='center',
ha='center',
bbox=dict(fc='w',boxstyle='round,pad=1'))
ax.text(1,0,
'False Pos: %d'%fp,
va='center',
ha='center',
bbox=dict(fc='w',boxstyle='round,pad=1'))
ax.text(1,1,
'True Pos: %d\n(Num Pos: %d)'%(tp,NP),
va='center',
ha='center',
bbox=dict(fc='w',boxstyle='round,pad=1'))
# Fill in secondary metrics: accuracy, true pos rate, etc...
ax.text(2,0,
'False Pos Rate: %.2f'%(fp / (fp+tn+0.)),
va='center',
ha='center',
bbox=dict(fc='w',boxstyle='round,pad=1'))
ax.text(2,1,
'True Pos Rate: %.2f'%(tp / (tp+fn+0.)),
va='center',
ha='center',
bbox=dict(fc='w',boxstyle='round,pad=1'))
ax.text(2,2,
'Accuracy: %.2f'%((tp+tn+0.)/N),
va='center',
ha='center',
bbox=dict(fc='w',boxstyle='round,pad=1'))
ax.text(0,2,
'Neg Pre Val: %.2f'%(1-fn/(fn+tn+0.)),
va='center',
ha='center',
bbox=dict(fc='w',boxstyle='round,pad=1'))
ax.text(1,2,
'Pos Pred Val: %.2f'%(tp/(tp+fp+0.)),
va='center',
ha='center',
bbox=dict(fc='w',boxstyle='round,pad=1'))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()… and here’s the code that generates the above example:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from show_confusion_matrix import show_confusion_matrix
rs = np.random.RandomState(1234)
p = 2
n = 200
py1 = 0.6
mean1 = np.r_[1,1.]
mean0 = -mean1
# generate training data
Y = (rs.rand(n) > py1).astype(int)
X = np.zeros((n,p))
X[Y==0] = rs.multivariate_normal(mean0, np.eye(p), size=(Y==0).sum())
X[Y==1] = rs.multivariate_normal(mean1, np.eye(p), size=(Y==1).sum())
lr = LogisticRegression()
lr.fit(X,Y)
# generate test data
Y = (rs.rand(n) > py1).astype(int)
X = np.zeros((n,p))
X[Y==0] = rs.multivariate_normal(mean0, np.eye(p), size=(Y==0).sum())
X[Y==1] = rs.multivariate_normal(mean1, np.eye(p), size=(Y==1).sum())
C = confusion_matrix(Y,lr.predict(X))
show_confusion_matrix(C, ['Class 0', 'Class 1'])